TYPES AND SOURCES OF CONTAMINATION

New liquid isn't perfect liquid. Generally, a new liquid that we get right out of the container isn't adequate for usage in hydraulic and lubrication arrangements. Added substances in a hydraulic liquid usually have the size of 1 micro and these substances are not affected by the methods of standard filtration.

SOLID PARTICLES:
There are two main classifications of particulate contamination. One is "silt" and other is "chips". "Silt" is stated as the gathering of particles that are not more than 5um in a time. Silt contamination can also cause the failure of a system component in time.
On the other hand “chips” are the particles that are more than 5+ and it can cause instant catastrophic failure. In case, these particles are not accurately reddened, contaminants commencing since industrial plus assemblage will remain in the operation. The contaminants consist of built-up, welding slag, particles of rubber or plastics that are used in hosepipes besides sealing, sand particles as of forming, and metallic junks from machined sections. Furthermore, if the liquid is added in the beginning to the system, it is considered as the introduction of contamination.
During operation of the system, contaminations come in from different openings as breather tops, worn seals, and opening of other operations. Internal contaminations are generated during system operation. This happens as the part when wear trash and chemical outcomes act in response with component planes for generating additional contamination.
SOURCES:
Sources of contaminations are as followed:
- Built-in in the course of industrial and assembly procedures.
- Added when new liquid is incurred.
- Consumed as outer the structure throughout the process.
- “Internally” produced throughout activity (as given in chart down).
GENERATED CONTAMINATION:
Contamination can be generated through:
- “Abrasive Wear” Firm atoms joining two effective planes, rubbing either separately otherwise jointly.
- “Cavitation Wear” Limited firth pouring into pump resulted in liquid vacuums that eventually collapse and triggering shockwaves that breakdown basic superficial substance.
- “Fatigue Wear” Atoms joining a slack may be resulted in the rise of surface stress that converts into expanded spall because of the damaged area which repeats its stress.
- “Erosive Wear” in case of adequate particles that flow in a fast stream of liquid destroy a metering edge or essential surface.
- “Adhesive Wear” Oil loss film permits “metal to metal” interaction in two moving objects.
- “Corrosive Wear” Water or substance contagion in the liquid has resulted in rust or a synthetic response that debases a surface.
WARNING SIGNALS:
Warning Signals can be as followed:
- Electro-magnet burn-out.
- Valve roll decentering
- spillage, “babbling”
- Failure of “Pump”, flow defect, regular replacement.
- Leakage in the cylinder, getting.
- Improved in “servo hysteresis”.
Utmost structure ingression enters a framework thru the traditional supply breather tops plus the pipe pole glands.
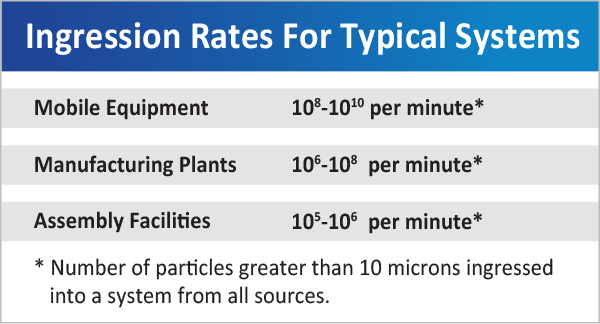
PREVENTIONS FOR CONTAMINATION:
There are some preventions, described as following:
- Use turn-on or a desiccants style strainers for flexible air breathers.
- Remove all systems, earlier than starting up.
- Identify pole wipers and switch seals of the worn actuator.
- Put caps on hoses and other manifolds in the course of handling and repairing.
- Before entering the new liquid into the reservoir, filter it.
WATER CONTAMINATION
There is something completely different to actual fluid preservation than just taking away the particulate issue. Fundamentally, water is a general and most common contaminant, and much like solid element contaminants, ought to be confiscated from working liquids. Water has the condition of the split up condition and free condition. Free or combined, water can be described as the water over the inundation reason for a selected liquid. Presently, the fluid can’t be separated or preserved large volume of water. Free water can be normally discernible like "milky" staining of the liquid.

Visual Effects Of Water In Oil

A simple “crackle check” can let you know whether there’s free water to your liquid. Put a flame underneath the instrumentality (container or flask). In case bubbles escalate and they crackle due to the instant of implemented temperature, it will indicate that water is free and it is existing in the liquid. “Hydraulic liquids” have the power for maintaining water as heat will increase. The milky liquid would possibly be clear as a machine heats up.
DAMAGES:
Water contamination may cause damages as:
- Decomposition of metal surfaces
- Intensified rough wear Enduring exhaustion
- Liquid added substances dissolution
- Fluctuation in viscosity
- The escalation in electrical conduction
"Anti-wear" added substances are separated from the water as well as structure acids. The blending of water, heat as well as the distinct metals supports the galvanic activity. Eroded and rusted metals surfaces and completions effects. Additionally, difficulties arise as temperature declines, therefore, the liquid has not much capacity to maintain water. As the water reaches its freezing point, crystals of ice are formed, inadequately, distressing the whole functioning of the system. It slows down working capacity or makes it inconsistent. Electric conduction turns into trouble when water defilement debilitates the protecting properties of a liquid, that's effecting its dielectric kilovolt power.

Predictable outcomes of pump wear because of particulate as well as water contamination.

SOURCES:
- Sported mechanism lids
- Reservoir gap/ spillage
- Condensing process
- Heat exchanger gap/ spillage
Liquids are perpetually presented to water and vapour whereas, being operated as well as saved. For example, outside storage of tanks and barrels is normal. Water might remain on the height of drums while changing in temperature, it would be brought into the drums. At the time of opening or filling of those drums, water might be presented.
Water could be entered into a mechanism via sported chamber, mechanism lids, or thru reservoir gaps. Process of condensing is also a main resource of water. As the liquid cools down in the container or drums, vapour can moderate the inside surfaces, resulting in the erosion or rust issues.
Free water" has much density as compared to oil, that's why water can settle to the base of the tank was quite a bit of it effectively, be evacuated through the drain valve opening. Assimilation filter components have ideal execution in the low stream as well as low consistency applications.
PREVENTIONS:
Unnecessary water can typically be evacuated through a mechanism. Comparable insurance gauges taken to limit the particulate tainting to enter in a structure could be functional in the water contamination. Regardless, when absurd water is perceived, it could normally abstain through one of the following strategies:
ABSORPTION:
Absorption can be done through filter essentials which are explicitly planned to separate free water. For the absorption process, a laminate type material has usually used that help to convert free water in the form of a gel, that gel is wrapped inside the component. These components are appropriate for standard filter frames and are commonly used in case of small volumes of water.
CENTRIFUGATION:
With the help of spinning motion, it separates water and oil. This method is effective if the volume of water is large and free.
VACUUM DEHYDRATION:
By using a vacuum dehydration process we can split up water and oil. This method is effective for free, dissolved and larger volumes of water.
AIR CONTAMINATION:
Air can exit into two forms either it can be a dissolved form or can be undissolved means it can be in Free State in a fluid system. “Dissolved air” may not cause any issue or a problem, which help it to remain in solution. When fluid has contained undissolved air, it causes problems as it travels in system components. Pressure changes can compress the air and then it can produce high temperature in insignificant bubbles of air. This high temperature helps to abolish substances and the base liquid.
In case the dissolved air volume ends up being adequately high, it will negatively affect the measure of work executed by the system. In a hydraulic system, the performance of work depends on the relatively incompressible liquid, but air decreases the greater part of the fluid. Because air is extra compressible as compared to fluid in which air is dissolved. In the presence of air, a pump stops performing its work for compressing the air and do less meaningful tasks in a system. In this case, we called the system ‘spongy’.
DAMAGES:
Air contamination may cause the following damages:
- transmitted power loss
- Reduction in pump output
- lubrication loss
- Increase in the operating temperature
- Formation of reservoir fluid
- Chemical responses
Air is act as the “potential source of oxidation” in fluids. Which causes erosion in parts of metal, in the presence of water this process becomes faster. Additionally, oxidation of substances may happen. Both processes generate oxides which help to support the particulates formation and structure a slurry within the fluid. To decrease wear as well as interference, it is necessary to remove oxidation debris.
SOURCES:
The following are the sources of air contamination:
- Leakage of system
- Pump aeration of pump
- Reservoir fluid instability
PREVENTIONS:
There are some preventions:
- System of air drains
- Flooded pull pump
- Design of proper reservoir
- Returning of line diffusers
